TREATMENTS
Bone Infection: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Symptoms of Bone Infection
Bone infections may develop suddenly (acute) or over time (chronic), each presenting distinct symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Localized pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Swelling and redness, sometimes accompanied by warmth
- Fever and chills, particularly in acute cases
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Limited movement or functional impairment in the affected limb
Chronic osteomyelitis may exhibit these symptoms mildly or intermittently, making it challenging to detect without medical imaging.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
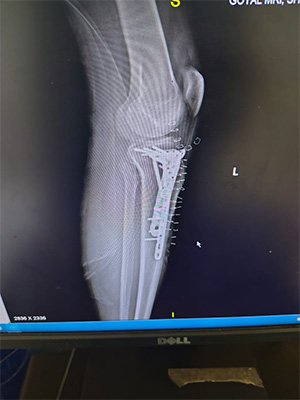
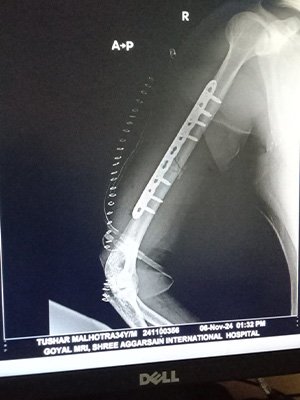
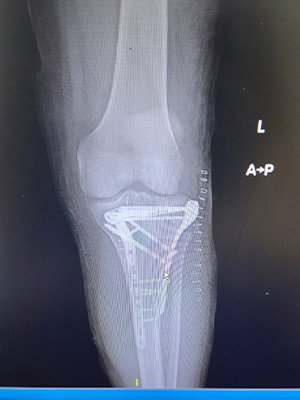
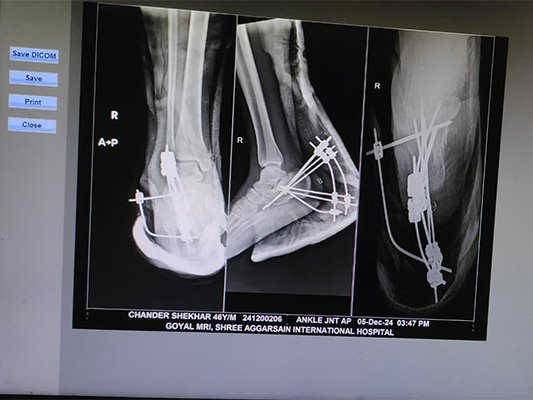
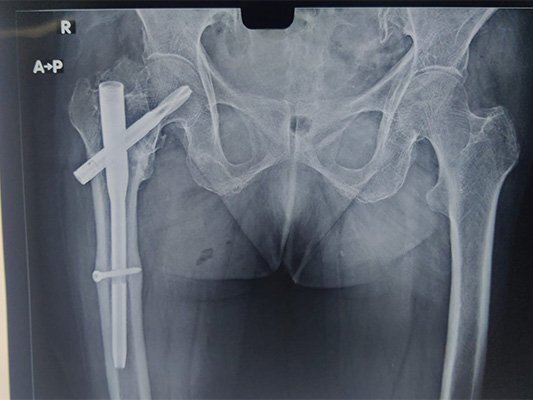
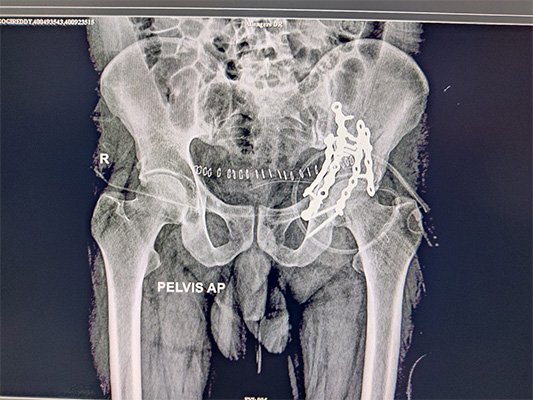
At Bansal Bone & Joint Clinic, Dr. Amit Bansal emphasizes a thorough diagnostic approach. Initial evaluation includes blood tests, imaging studies like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, and sometimes a bone biopsy to determine the infection’s extent and origin.
Treatment for osteomyelitis combines antibiotics, sometimes given intravenously to ensure effective delivery to the bone tissue. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to remove infected tissue, drain abscesses, or reconstruct damaged bone areas. Chronic cases may require more extensive surgical intervention or prolonged antibiotic courses.